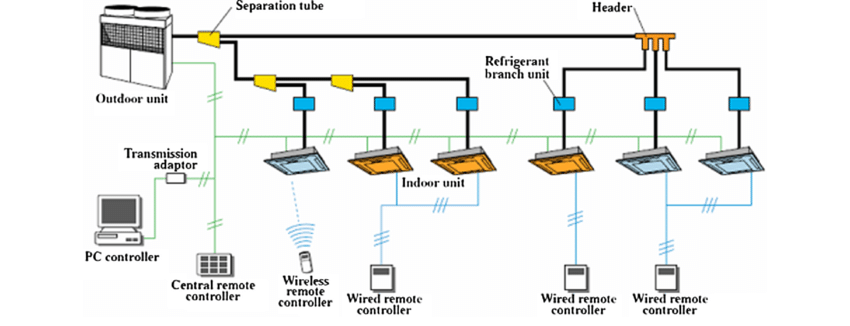
The energy consumption of air-conditioning systems has gained increasing attention as it contributes significantly to the global building energy use. The variable refrigerant flow (VRF) system is a common air-conditioning system applied widely in residential and office buildings in China. Understanding the actual operation and performance of VRF systems is fundamental for the energy-efficient design and operation of VRF systems. Previous research on VRF system operation used either limited field data covering certain building types and climate zones or used a questionnaire to obtain a larger dataset. However, they did not capture the wide applications of VRF systems quantitatively across all building types, climate zones, and operating conditions.